A device for measuring battery capacity from AliExpress. Car battery capacity meter Device for determining the capacity of a 6v battery
Every car owner wonders what kind of device is needed to measure battery capacity. This value is often measured during scheduled maintenance, but it will be useful to learn how to determine it yourself.
Battery capacity measuring device
Battery capacity is a parameter that determines the amount of energy supplied by the battery at a certain voltage in one hour. It is measured in A/h (Ampere per hour), and depends on which it is determined by a special device - a hydrometer. When purchasing a new battery, the manufacturer indicates all technical parameters on the case. But you can determine this value yourself. There are special devices and methods for this.
The easiest way is to take a special tester, for example "Pendant". This is a modern device for measuring the capacity of a car battery, as well as its voltage. In this case, you will spend a minimum amount of time and get a reliable result. To check, you need to connect the device to the battery terminals and within a few seconds it will determine not only the capacity, but also the battery voltage and the condition of the plates. However, there are other battery capacities.
First method (classic)
For example, a multimeter can be used as a device to measure the capacity of a car battery, but you will not get accurate readings with it. A prerequisite for this method (it is called the control discharge method) is that the battery is fully charged. First, you need to connect a powerful consumer to the battery (a regular 60W light bulb will do).

Afterwards, you need to assemble a circuit, which consists of a multimeter, battery, consumer, and apply the load. If the light bulb does not change its brightness within 2 minutes (otherwise the battery cannot be restored), we take readings from the device at certain time intervals. As soon as the indicator drops below the standard battery voltage (under load it is 12V), its discharge will begin. Now, knowing the period of time that was required to completely deplete the energy reserve and the load current of the consumer, it is necessary to multiply these values. The product of these quantities is the actual capacity of the battery. If the obtained values differ from the passport data to a lesser extent, the battery must be replaced. This method makes it possible to determine the capacity of any battery. The disadvantage of this method is that it takes a lot of time.
Second method
You can also use a method in which the battery is discharged through a resistor using a special circuit. Using a stopwatch, we determine the time spent on the discharge. Since energy will be lost at a voltage within 1 Volt, we can easily determine it using the formula I=UR, where I is the current, U is the voltage, R is the resistance. In this case, it is necessary to avoid completely discharging the battery, using, for example, a special relay.
How to make the device yourself
If it is not possible to purchase a ready-made device, you can always assemble a device for measuring battery capacity with your own hands.
To determine the state of charge and capacity of the battery, you can use There are many models of ready-made plugs on sale, but you can assemble it yourself. One of the options is discussed below.

This model uses an extended scale, which ensures high measurement accuracy. There is a built-in load resistor. The scale is divided into two ranges (0-10 V and 10-15 V), which provides an additional reduction in measurement error. The device also has a 3-volt scale and another measuring device output, making it possible to check individual battery jars. The 15V scale is achieved by reducing the voltage on the diode and zener diode. The device current increases if the voltage value exceeds the opening level of the zener diode. When a voltage of incorrect polarity is applied, the diode performs the protective function.
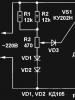
In the diagram: R1- transfers the required current to the zener diode; R2 and R3 - resistors selected for the M3240 microammeter; R4 - determines the width of the narrow scale range; R5 - load resistance, switched on by toggle switch SB1.
The load current is determined by Ohm's law. Load resistance is taken into account.

AA battery capacity measuring device
The capacity of AA batteries is measured in mAh (milliampere per hour). To measure such batteries, you can use special chargers that determine the current, voltage and capacity of the battery. An example of such a device is the AccuPower IQ3 battery capacity measuring device, which has a power supply with a voltage range from 100 to 240 Volts. To measure, you will need to insert batteries into the device, and all the necessary parameters will appear on the display.

Determining capacity using a charger
The capacity can also be determined using a conventional charger. Having determined the amount of charge current (it is indicated in the characteristics of the device), it is necessary to fully charge the battery and note the time spent on this. Then, multiplying these two values, we get the approximate capacity.
More accurate readings can be obtained using another method, for which you will need a fully charged battery, a stopwatch, a multimeter and a consumer (you can use, for example, a flashlight). We connect the consumer to the battery, and using a multimeter we determine the current consumption (the lower it is, the more reliable the results). We note the time during which the flashlight was shining, and multiply the resulting result by the current consumption.
How and why is battery capacity measured?
Charge Q, as the amount of electricity, is measured in coulombs (C), the electrical capacity of capacitors C is in farads, microfarads (μF), but for some reason it is measured not in farads, but in ampere-hours (milliamp-hours).
What would that mean? One ampere is a coulomb in one second; we know from a physics course that if an electric charge equal to 1 coulomb passes through a conductor in 1 second, then a current of 1 ampere flows through the conductor.
So what is an ampere hour then? Ampere-hour (Ah) is the battery capacity at which, based on a reduced current of 1 ampere, the battery will be discharged in 1 hour to the minimum permissible voltage.

1 ampere hour is 3600 coulombs. Suppose we want to obtain a bank of capacitors that is equivalent in discharge characteristics, albeit over a short section, to a 12-volt battery with a capacity of 55 ampere-hours. 55 amperes for an hour is 55 * 3600 coulombs.
Let us assume a voltage change from 13 to 11 volts, then since Q = C(U1-U2), then C = 55 * 3600/2 = 99000 F. Almost 100 kilofarads is the equivalent electrical capacity of a car battery, if its discharge characteristics were the same as at the capacitor.
There is a video on the Internet where six supercapacitors of 3000 F, 2.7 V each, connected in series, replace the starter battery of a car. It turns out 500 F at about 16 V.
Let's estimate what current and for how long such an assembly can produce. Let the operating range be taken again from 13 to 11 volts. For how long can you count on a current of 200 A (with a margin)? I = C(U1-U2)/t, then t = C(U1-U2)/I = 500*2/200 = 5 seconds. Enough to start the engine.
Lead-acid batteries, at first glance, are very simple in design. But the downside of such simplicity is the need to strictly adhere to certain rules for operating the battery. Only then will it implement the number of charge-discharge cycles declared by the manufacturer, and sometimes will show the best result. This will require additional equipment, which will be discussed in the article.
Sulfation of battery plates
The main danger that exists for a lead-acid battery is storing the device in a discharged state. In this case, the process of so-called sulfation occurs - the deposition of lead sulfate (PbSO4), which is a dielectric, on the plates. The minimum permissible voltage at the battery terminals is usually given in its documentation. For example, for most lead-acid batteries with a nominal voltage of 12.6 V, the minimum voltage after which the process of intensive sulfation of the battery plates begins is 10.8 V.
Measuring voltage and internal resistance of batteries
The simplest type of battery monitoring is to measure the EMF at its terminals. When the EMF is less than the minimum permissible level, the battery is recharged to the rated voltage at the terminals. But this method is only suitable for known good batteries. If the plates are already coated with a thick layer of lead sulfate, then the battery will have high internal resistance. In this case, the EMF at the terminals may be at the nominal level, but the battery will quickly discharge or will not be able to provide the required current to the load at all. A voltmeter will not be able to detect this. However, if sulfation on the plates is detected in a timely manner, the battery can still be saved, which will be discussed below.
To monitor the battery with the ability to quickly detect a malfunction, a special device is required. In addition to the terminal voltage, it must measure the internal resistance (or conductivity) of the battery. By comparing the measured values with those given in the documentation for the battery, we can draw a conclusion about the suitability of the battery for further use. An example of such a device is PITE 3915. Its important advantages are the presence of a large color LCD display and a comfortable keyboard.

Often, speeding up work requires not only the data itself, but also an assessment of whether it is outside acceptable limits. In this case, the Fluke BT500 Series meters are a good choice.

The user can set threshold values for 10 parameters, after each of which the device issues a warning. Another feature of the Fluke BT500 series is the charger ripple measurement feature. It is possible to measure charge-discharge cycles for several batteries at once. In this case, for each battery, its own profile is created in the device’s memory, in which the data of sequential measurements are accumulated. In addition to the basic Fluke BT510, the series includes the Fluke BT520 for measuring batteries installed in cabinets and other hard-to-reach areas, as well as the Fluke BT-521 with advanced features. The Fluke BT520 and BT521 come with an interactive probe (BTL20 and BTL21, respectively) and a carrying case. A special feature of the Fluke BT521 is its temperature measurement functions, as well as wireless communication with a mobile device.
The dependence of the current flowing through the battery on the potential difference at its terminals is a nonlinear quantity. Therefore, the internal resistance of the battery, measured by direct current, is rather an estimate, since it depends on many factors. For many practical applications, such accuracy is sufficient - a decision is made whether the battery is working or faulty. But, if you want to understand whether it's worth bothering with restoring the battery, you need to more accurately measure the internal resistance. You can increase the accuracy of measuring the internal resistance of a battery if you do it on alternating current. This is exactly the method implemented in the PITE BT-301 device. Another important feature of the device is the presence of an additional function for testing nickel-cadmium batteries.

Instruments for measuring battery capacity
The devices listed above require their readings to be interpreted in a certain way to make a decision. For this, firstly, you need highly qualified personnel, and, secondly, documentation for the battery so that you have something to compare the measured parameters with. But there are also easy-to-use battery testers that measure battery voltage and capacity. In this case, it is enough to attach the tester to the battery terminals for a few seconds. Next, the capacity and voltage are compared with those indicated on the battery case.
The disadvantage of this method of testing batteries is that it uses a method for measuring capacity, which is characterized by low accuracy and operates within a limited range of capacities. Nevertheless, the capabilities of such a tester are quite sufficient for practical use.
An example of compact and easy-to-use battery capacity meters is the domestically produced “Pendant” series of devices. The measurement time is 4 s. During the measurement process, a signal of a special shape is sent to the battery. Based on the response, the active area of the plates is determined, based on which the capacitance is calculated.
It should be noted that for mission-critical applications, battery capacity measurements should be performed using a dedicated load, such as the PITE-3980. This device is capable of transmitting battery discharge data wirelessly.

Smart solutions for battery testing
If batteries are involved in critical systems, it is best to constantly monitor them. Modern technologies come to the rescue for this:

In order to measure the capacity of a battery, they usually do this: connect a resistor of a certain value to this battery, which discharges this battery, and recording the current flowing through the resistor and the voltage across it, wait until the battery is completely discharged. Based on the data obtained, a discharge graph is constructed, from which the capacity is determined. The only problem is that as the voltage on the battery decreases, the current through the resistor will also decrease, so the data will have to be integrated over time, so the accuracy of this method of measuring battery capacity leaves much to be desired.
If you discharge the battery not through a resistor, but through a source of stable current, this will allow you to determine the battery capacity with very high accuracy. But there is one problem - the voltage on the battery (1.2..3.7 V) is not enough to operate a stable current source. But this problem can be circumvented by adding an additional voltage source to the measurement circuit.
Rice. 1. Circuit for measuring battery capacity
V1 - battery under study; V2 - auxiliary voltage source; PV1 - voltmeter;
LM7805 and R1 - stable current source; VD1 - protective diode.
Figure 1 shows a schematic diagram of a setup for measuring battery capacity. Here you can see that the measured battery V1 is connected in series with the current source (it is formed by the LM7805 integrated stabilizer and resistor R1) and the auxiliary power source V2. Since V1 and V2 are connected in series, the sum of their voltages is sufficient to operate the current source. Since the minimum voltage required for the operation of the current source is 7 V (of which 5 V is the voltage at the output of the LM7805 microcircuit, i.e. in this case it is the voltage drop across resistor R1, and 2 V is the minimum permissible voltage drop between input and output of LM7805), then the sum of voltages V1 and V2 is sufficient with some margin to operate the current source.
Instead of the LM7805 stabilizer, you can use another integrated regulator, for example, LM317 with an output voltage of 1.25 V and a minimum voltage drop of 3 V. Since the minimum operating voltage of the current source will be 4.25 V, the voltage of the second voltage source V2 can be reduced to 5 B. If the LM317 stabilizer is used, the value of the stabilization current will be determined by the formula I = 1.25/R1
Then for a discharge current of 100 mA, the value of resistance R1 should be approximately 12.5 Ohms.
How to measure battery capacity
First, by selecting resistor R1, you need to set the discharge current - usually the value of the discharge current is chosen equal to the operating discharge current of the battery. It should also be borne in mind that some models of 7805 integrated voltage stabilizers can consume a small control current of the order of 2...8 mA, so it is recommended to check the current value in the circuit with an ammeter. Next, a fully charged battery V1 is installed in the circuit, and by closing switch SA1, they begin counting down the time until the voltage on the battery drops to a minimum value - for different types of batteries this value is different, for example, for nickel-cadmium (NiCd) - 1, 0 V, for nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) - 1.1 V, for lithium-ion (Li-ion) - 2.5...3 V, for each specific battery model, these data must be viewed in the appropriate documentation.
After reaching the minimum voltage on the battery, switch SA1 is opened. It should be remembered that discharging the battery below the minimum voltage can damage it. Multiplying the discharge current (in Amperes) by the discharge time (in hours) we obtain the battery capacity (A*h):
C=I*t
Let's consider the practical application of this method of measuring battery capacity using a specific example.
Measuring the capacity of the NB-11L battery
The NB-11L battery (Fig. 2) was purchased from the DealeXtreme online store for $3.7 (SKU: 169532). On the battery case its capacity is indicated - 750 mAh. On the website its capacity is indicated more modestly - 650 mAh. What is the real capacity of this battery?

Rice. 2. Li-ion battery NB-11L with a capacity of supposedly 750 mAh
Fits CAN.NB-11L 3.7V 750mAh
Use specified charger only
To connect the conductors to the battery contacts, you will need two paper clips, which should be bent as shown in Figure 3, and connected to the “+” and “-” terminals of the battery (Figure 4.). It is necessary to avoid shorting contacts; it is better to insulate them.
To measure the capacity of the NB-11L battery, its discharge current was taken to be 100 mA. For this purpose, the value of resistor R1 was chosen to be slightly more than 50 Ohms. The power dissipated by resistor R1 is determined by the formula P = V 2 /R1, where V is the voltage across resistor R1. In this case, P=5 2 /50=0.5 W. The LM7805 stabilizer should be installed on a radiator, but if there is no suitable radiator at hand, then the chip can be partially immersed in a glass of cold water, but so that the terminals remain dry (in the case of the TO-220 case).
After installing a fully charged NB-11L battery into the circuit and closing the SA1 switch, the countdown began with periodic voltage monitoring using the PV1 voltmeter. The data was entered into a table, according to which a graph of the discharge of the NB-11L battery was constructed (Fig. 5).

Rice. 5. Voltage graph on the NB-11L battery during its discharge with a current of 100 mA
From this it can be seen that after 5 hours of discharge with a current of 0.1 A, the voltage on the battery dropped to 3 volts and began to rapidly drop further.
C = I * t = 0.1 * 5 = 0.5 A = 500 mAh.
So the actual capacity of the NB-11L battery turned out to be 1.5 times lower than indicated on it.
Capacity is charge Q a new battery or a fully charged battery. Charge (amount of electricity) is measured in Coulombs: 1 Coulomb = 1 Ampere × 1 second. Capacity is usually measured in units of ampere hour or ma hour . The typical capacity of a AAA battery is 1000 mAh, AA - 2000 mAh. A 1000mAh battery can produce 1000mA for 1 hour or 100mA for 10 hours. Considering the voltage U, then we can estimate the energy stored in the battery E = Q × U
To determine the battery capacity, it is fully charged, then discharged with a given current. I, and measure time T, for which he was discharged. Product of current I for a while T and there is the battery capacity Q = I × T. The capacity of the battery is also measured, but after a complete discharge the battery can be charged again, but the battery can no longer be used. The point is that you measure capacity of batteries of this type. By the way, capacity alkaline batteries is approximately equal to the capacity of modern NiMh batteries of the same size - AA (2000 mAh), AAA (1000 mAh).
Circuit for measuring capacitance
The proposed circuit discharges the battery through a resistor R to the voltage of almost complete discharge of the NiCd or NiMh element - approximately 1 volt. The discharge current is equal to I = U / R. (About selecting the discharge current) To measure the discharge time T watches operating on a voltage of 1.5-2.5V are used. To protect the battery from complete discharge, a PVN012 solid-state relay is used. It turns off the battery when the voltage drops U to the minimum permissible Ue = 1V.
How it works
The battery must be fully charged and connected to the device. The clock must be set to 0 and the button pressed Start . At this moment, the relay closes contacts 4-5 and 5-6. The battery begins to discharge through a resistor R and voltage is supplied to the clock. The voltage across the battery and resistor gradually decreases. When the voltage across the resistor R drops to 1V, the relay opens the contacts. The discharge stops and the clock stops.
As the battery discharges, the control current through relay contacts 1-2 decreases from approximately 8 to 2mA. With a control current of 3mA, the resistance of contacts 4-5 and 5-6 is less than 0.04 Ohm. This is small enough not to be taken into account when calculating the current - if you need a discharge current of 1A, take a resistor R=1.2 Ohm.
After the discharge stops, the voltage on the battery increases to 1.1-1.2V due to the internal resistance of the cell.
Contact losses
When repeating this circuit, take measures to reduce the resistance of the battery contacts and connectors. With a current of 0.5-1A, 0.1V or more can be lost on the contacts, which will deteriorate the measurement accuracy. The same type of loss is caused by the steel spring used in some battery holders. The spring and other steel contacts must be bridged with copper wire. I did one of the options AA and AAA battery capacity meter in the case from a simple charger that had good copper contacts.
Additional questions
Self-discharge
Please note that the capacity freshly charged batteries are higher, since over time some of the charge is lost due to self-discharge. To find out the amount of self-discharge, you need to measure the capacity immediately after charging, and measure again a week (month) after charging. Self-discharge of NiMh batteries can reach 10% per week or more.
How accurately is capacitance measured?
The exact amount of electricity can be determined by integrating over time dQ = 1/R × U(t) × dt.
The experimental discharge graphs show that as the discharge progresses, the voltage decreases from approximately 1.4V to 1.0V. The discharge current U/R also decreases. When used as medium voltage nominal Values of 1.2V result in an accuracy of no worse than 10%. This is true if the battery is used at approximately the same discharge current as when measuring capacity.
Example of discharge graphs 
If during measurement there was a current of 0.5A, and when using 5A, then the battery will discharge several times faster than expected. At a current use of 0.05A, the capacity will be greater than when measured. At a current of 0.005A, the capacity may be less than measured due to self-discharge of the battery over a long period of operation. A significant difference between the measurement current and the operating current introduces an error of more than 10%.
Using steel contacts in the device instead of copper can increase the error by 10% or more, especially with a high discharge current.
Some error in the cutoff voltage value of 1.0V is associated with the dependence of the current-voltage characteristic of the solid-state relay on temperature. Under room conditions, this gives an error of 1-2%.

What should the discharge current be?
It is necessary to choose the current at which this battery is usually used. If the discharge current is too high, the internal resistance will cause the battery voltage to quickly drop below 1 volt and the measured capacitance value will be low. If you select too low a discharge current, the measured capacity will be greater than the battery will actually produce when operating in your device.
Why two diodes?
Diodes are used to protect the solid state relay in case of accidental resistor breakage R. If you are sure that a break is impossible, or you are measuring the capacity of batteries with a voltage of less than 1.4V ( one AA or AAA element), then the diodes can be removed. In this case, the circuit is placed inside the alarm clock, as I did before. A 5 ohm resistor protects the relay when the Start button is pressed. It can also be removed if you turn on the button parallel to pins 4-5, as in the simplified diagram.
How to measure the capacity of a lithium-ion battery?
| Um | Ue | I | R | r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 6.0 | 0 |
| 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 2.4 | 0 |
| 3.3 | 3.0 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 4.4 |
| 8.4 | 7.0 | 0.1 | 12 | 72 |
In this case, a voltage divider is connected to the battery according to the example shown in the diagram. Using a voltage divider, you can measure the capacity of a multi-cell battery or the capacity of a lithium-ion battery.
Required discharge current I at medium voltage Um provides the sum of two resistors: R + r = Um / I.
Resistor R is calculated so that at the final voltage on the battery Ue, voltage across the resistor R became equal to 1V: R = (Um / I) × (1V / Ue).
How to check battery capacity by voltage?
Capacitance cannot be determined by voltage. Each type of battery and accumulator has typical discharge curves. From them you can estimate the ratio of charge to capacity ( charge percentage). I'm using a charger Ansmann, which for such an assessment measures the voltage at a given discharge current. However, in NiMh batteries, not only the capacity, but also the operating voltage decreases with age. In some cases, Ansmann gave an estimate of 30%, while the measurement before full discharge gave 80%.
How to measure battery capacity without this circuit?
Connect a resistor to the charged battery R and a voltmeter. Keep an eye on the clock. Over time T voltage U will drop to the minimum acceptable. At this point, disconnect the resistor. Capacitance is Q = T × U / R