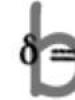What you need to know about the chassis of cars. The suspension structure, how it works and what the car's chassis consists of
Includes frame, front axle (front axle), rear axle (rear axle), front suspension, rear suspension, wheel hubs, wheels and tires. The main load-bearing element of a car is the frame or body.
Truck bodies typically consist of a driver's cab and a cargo box. Depending on the vehicle layout, there are hooded and hoodless cabs. The cabin is fixed to the frame so that frame distortions do not cause its destruction. On modern trucks, the driver's cab is secured with springs and shock absorbers. The truck body has a base connected to the floor. It forms a platform, folding sides and a rigidly fixed front side.
Vans have a base, frame and cladding, for which plywood, plastic, duralumin and other materials are used.
For the manufacture of passenger car bodies, frame and frameless structures are used. Frame structures provide better insulation of the body from vibration loads, frameless structures provide the lowest vehicle weight. The type of passenger car is determined by the volume of functional compartments and design. According to the number of body volumes, perform three-volume, two-volume and one-volume.
A three-volume body includes the engine compartment, interior and trunk, a two-volume body includes the engine compartment and interior, and a single-volume body combines all three functional volumes. Passenger car bodies can be of the following types: closed, fully opening and cargo-passenger.
The front axle (front axle) is used to install steering wheels on trucks. It transmits longitudinal and lateral forces that arise when the vehicle moves through the suspension to the frame from the wheels. The front axle is an I-section steel beam with the ends bent upward.
At the ends of the axle, rotating axles are secured to the eyes with pins. Wheel hubs are installed on their axle through two tapered roller bearings, which are secured with a nut with a locking pin. To make it easier to control the car, the pivot pins of the steering axles have longitudinal and transverse inclinations, which allow the wheels of the car to take a position corresponding to straight motion. To unload the outer bearing of the wheel hub, the axles of the axles are tilted with their ends down (wheel camber).
The wheel fastening must ensure the accuracy of wheel centering, the ability to control the condition of the fastening, stability of tightening, reliability, ease of installation and removal of the wheel. Disc wheels are secured to the hub flange with nuts and bolts or studs pressed into the hub flange.
The wheel fastening is centered along the spherical or conical chamfers of the mounting holes, the central hole of the disk and the cylindrical surface of the disk mounting holes.
Car chassis – Wheel balancing.
During the balancing process, wheel imbalance is eliminated. Tire imbalance manifests itself in vibration and bouncing of the car, deterioration in comfort, increased fuel consumption, and reduced service life of tires, shock absorbers, and steering. The influence of these negative phenomena increases with increasing vehicle speed.
Car chassis – Tires.
A tire consists of a carcass, belt, tread, sidewalls, valve, inner tube or sealing layer, and rim tape. Tube and tubeless tires mounted on the rim must be sealed and provide a specified stability of internal pressure over time; tire adhesion to the road surface should be sufficient, and rolling resistance should be minimal; the tire must provide a low specific load in contact with the road; tire runout should not exceed the permissible values for the type of tire, and the noise level when driving should be within acceptable limits; the tire must be convenient for assembly and disassembly; it must have sufficient strength, resist punctures and other types of damage, and be durable; The tire tread pattern must match the road surface.
Tires are classified by purpose (for cars, trucks, off-road vehicles); by sealing method (chamber, tubeless); by profile ( regular profile, wide profile, pneumatic roller, arched, ultra-low profile); by size (large-sized, medium-sized, small-sized); by design (diagonal, radial, with a removable tread in the frame, frameless, with adjustable pressure).
What is important for tires is service life, reliability, low rolling resistance, safety, efficiency, ensuring the optimal diameter for a given load capacity, and comfort. Pneumatic radial and diagonal tires are marked on each tire, which includes the manufacturer's trademark, tire designation, and model.
Currently, tubeless radial tires are being developed, improved and used. Tubeless tires require a special deep rim that provides full sealing while being easy to assemble. If tires with adjustable pressure are installed, the vehicle must be equipped with a device for supplying air to the tire when parked and while driving. This device uses compressed air from the brake compressor.
The article uses materials from open sources: (Viktor Baranovsky. Car. 1001 tips)
The chassis is a connecting chain running from the wheels to the body. The chassis of the car absorbs all the unevenness of the road surface. Thanks to this unit, the driver may not even feel collisions or hitting minor bumps. And in order for you to feel only comfort while driving throughout the entire operation of the vehicle, you need to know what the structure of the vehicle’s chassis is and from time to time check the condition of all parts of this unit. In this article I will try to explain in the most accessible way for every driver, regardless of experience, what it is and what elements and components are associated with this part of the car.
There is a very big recommendation for drivers: always listen for knocks, squeaks or malfunctions of the car. This will allow you to contact a service station at the right time and fix the problem that has just appeared. This is especially true for the chassis, since it is the shell that keeps the vehicle moving.
The chassis structure consists of the following elements:
- Wheels;
- Bridge;
- Frame or body;
- Suspension.
The chassis may also include other, additional elements, but it is these parts that play the main role in creating comfort and ease of control. Each of these elements performs a separate function, but their work is designed to minimize vibration, oscillation, and shaking of the vehicle while driving. This is the chassis diagram.
The frame and body are the backbone of the entire mechanism, since it is to it that the main elements of the vehicle suspension are attached. The frame is a direct element that takes part in the formation of the chassis. As a rule, it is generally accepted that frames do not belong to passenger cars. They are commonly seen on trucks. For passenger cars, it is customary to use the word “body”. And it is to the body that all other parts that relate to such a thing as the chassis of the car are attached. All other elements are connected to the frame.
In order for the body to withstand all the hardships of our roads, some of its elements must be made of durable iron.
In other areas, profile sheets can be used as cladding, as they are highly resistant to corrosion. 
Suspension and its purpose: it is this element of the chassis system that allows the driver to more smoothly tolerate all the unevenness of the road surface. The suspension is used to soften or dampen vibrations, the appearance of which is provoked by unevenness on the surface of the roadway. This occurs due to the fact that the suspension eliminates rigid adhesion between the wheels and its body, at the expense of other parts.
Depending on the type or version of suspension installed on your vehicle, these bumps may not be noticeable to the driver. The service life of the suspension is long, but how long the suspension of your car will last depends only on you. In order to extend this period as long as possible, you need to operate the vehicle in accordance with the requirements and from time to time carry out diagnostics not only of the suspension components, but also of all components and parts of the vehicle. 
Today it is customary to distinguish between two types of suspension: independent and dependent. Vehicles with dependent suspension have rear wheels connected to each other by a special connecting beam. The suspension of vehicles whose wheels are not connected by a beam is called independent.
Axles not only connect two wheels, but also perform a supporting function for the vehicle frame. They can be attached to the car, directly to the frame itself (on a truck) or to the body, in the case of a passenger vehicle.
It's no secret that these parts of the car are the first suspension elements that feel the whole situation on the road. It is the wheels that fall into holes and run over hills. Therefore, first of all, they suffer. Depending on how you operate the vehicle, the service life of the wheels and related parts directly depends. The rougher its exploitation, the shorter this period will be. To preserve your suspension, you need to take good care of your vehicle, be sure to undergo timely maintenance and listen to the car’s performance, so that in the future you don’t have to spend money on repairs and such precious time.
Principle of operation
The main role in creating a comfortable ride is played by the suspension. This device dampens vibrations arising from uneven surfaces.
The chassis allows the car to move, while creating comfortable conditions for the driver and passengers. Knowledge of the system as a whole, the scheme of its operation and its component elements is not necessary for every driver, but if you know all this, it will help you control the car correctly and cope with any difficulties that arise on the road. The structure of this part is not as complicated as it seems; any specialist at a service station or even a familiar driver can tell you about it, but it is better to refer to the manual for your car to know the details of your specific model. Good luck and take care of your car!
Video “How a car’s chassis works”
After watching the recording, you will learn how the steering system of a car functions and what elements it consists of.
The road along which the driver chooses a route is not always level and smooth. Very often, it may contain such phenomena as uneven surfaces - cracks in the asphalt and even bumps and potholes. Don't forget about speed bumps. This negative would have a negative impact on driving comfort if there were no shock-absorbing system - the car's suspension.
Purpose and device
While driving, road unevenness in the form of vibrations is transmitted to the body. The vehicle's suspension is designed to dampen or soften such vibrations.
A car suspension is a technically complex unit that has the following structure:
- elastic elements - metal (springs, springs, torsion bars) and non-metallic (pneumatic, hydropneumatic, rubber) parts, which, due to their elastic characteristics, take the load from road unevenness and distribute it to the car body;
- damping devices (shock absorbers) - units that have a hydraulic, pneumatic or hydropneumatic structure and are designed to level body vibrations received from an elastic element;
- guide elements - various parts in the form of levers (transverse, longitudinal) that provide connection between the suspension and the body and determine the movement of the wheels and body relative to each other;
- anti-roll bar - an elastic metal rod that connects the suspension to the body and prevents the car from increasing roll while driving;
- wheel supports - special steering knuckles (on the front axle) that absorb the loads coming from the wheels and distribute them over the entire suspension;
- fastening elements for parts, components and assemblies of the suspension are means of connecting suspension elements with the body and among themselves: rigid bolted connections; composite silent blocks; ball joints (or ball joints).
Principle of operation
The operation of a car suspension is based on the conversion of the impact energy arising from a wheel hitting an uneven road surface into the movement of elastic elements (for example, springs). In turn, the rigidity of the movement of elastic elements is controlled, accompanied and softened by the action of damping devices (for example, shock absorbers). As a result, thanks to the suspension, the impact force that is transmitted to the car body is reduced. This ensures smooth running. The best way to see the system in action is to use a video that clearly demonstrates all the elements of a car's suspension and how they interact.
Cars have suspensions of varying stiffness. The stiffer the suspension, the more informative and efficient the car control. However, this seriously compromises comfort. And, on the contrary, the soft suspension is designed in such a way that it provides ease of use and sacrifices controllability (which cannot be allowed). That is why car manufacturers are striving to find their best option - a combination of safety and comfort.
Variety of suspension options
The vehicle suspension device is an independent design solution of the manufacturer. There are several typologies of car suspension: they are distinguished by the criterion underlying the gradation.
Depending on the design of the guide elements, the most common types of suspension are distinguished: independent, dependent and semi-independent.
The dependent version cannot exist without one part - a rigid beam that is part of the car axle. In this case, the wheels move parallel in the transverse plane. The simplicity and efficiency of the design ensures its high reliability, preventing wheel alignment. That is why dependent suspension is actively used in trucks and on the rear axle of cars.
The independent suspension system of a car assumes that the wheels exist autonomously from each other. This improves the damping characteristics of the suspension and ensures a smoother ride. This option is actively used for organizing both front and rear suspension on passenger cars.
The semi-independent version consists of a rigid beam secured to the body using torsion bars. This scheme ensures relative independence of the suspension from the body. Its typical representative is the front-wheel drive VAZ models.
The second typology of suspensions is based on the design of the damping device. Experts distinguish hydraulic (oil), pneumatic (gas), hydropneumatic (gas-oil) devices.
The so-called active suspension stands apart. Its design includes variable capabilities - changing suspension parameters using a specialized electronic control system depending on the vehicle's driving conditions.
The most common parameters to change are:
- degree of damping of the damping device (shock absorber);
- the degree of rigidity of the elastic element (for example, a spring);
- degree of rigidity of the anti-roll bar;
- length of guide elements (levers).
Active suspension is an electronic-mechanical system that significantly increases the cost of the car.
Main types of independent suspension
In modern passenger cars, an independent suspension option is often used as a shock-absorbing system. This is due to the good controllability of the car (due to its low weight) and the absence of the need for total control over the trajectory of its movement (as, for example, in the case of a truck).
Experts distinguish the following main types of independent suspension. (By the way, the photo will allow you to more clearly analyze their differences).
Double wishbone suspension
The structure of this type of suspension includes two levers attached to the body with silent blocks, and a coaxially located shock absorber and coil spring. 
MacPherson strut suspension
This is a derivative (from the previous type) and a simplified version of the suspension, in which the upper arm was replaced by a shock absorber strut. Currently, MacPherson strut is the most common front suspension design for passenger cars. 
Multi-link suspension
Another derivative, improved version of the suspension, in which two wishbones were “separated” as if artificially. In addition, the modern version of the suspension very often consists of trailing arms. By the way, multi-link suspension is the most commonly used rear suspension design for passenger cars today. 
The design of this type of suspension is based on a special elastic part (torsion bar), which connects the lever and the body and works to twist. This type of design is actively used in organizing the front suspension of some SUVs. 
Front suspension adjustment
An important component of a comfortable ride is the correct adjustment of the front suspension. These are the so-called steering wheel alignment angles. In common parlance, this phenomenon is called “wheel alignment.”
The fact is that the front (steered) wheels are installed not strictly parallel to the longitudinal axis of the body and not strictly perpendicular to the road surface, but with certain angles that provide tilts in the horizontal and vertical planes. 
Correctly set wheel alignment:
- firstly, it creates the least resistance to vehicle movement, and, therefore, simplifies the process of driving;
- secondly, it significantly reduces tire tread wear; thirdly, it significantly reduces fuel consumption.
Installing corners is a technically complex procedure that requires professional equipment and work skills. Therefore, it should be performed in a specialized institution - a car service center or service station. It’s hardly worth trying to do this yourself using a video or photo from the Internet if you have no experience in such matters.
Suspension faults and maintenance
Let’s make a reservation right away: according to Russian legal norms, not a single suspension malfunction is included in the “List of…” malfunctions with which driving is prohibited. And this is a controversial point.
Let's imagine that the suspension shock absorber (front or rear) does not work. This phenomenon means that driving over every bump will be associated with the prospect of body rocking and loss of vehicle controllability. What can we say about the completely loose and unusable ball joint of the front suspension? The result of a malfunction of a part - “the ball has flown out” - threatens a serious accident. A broken elastic suspension element (most often a spring) leads to body roll and sometimes an absolute inability to continue moving.
The malfunctions described above are the final, most odious malfunctions of the car suspension. But, despite their extremely negative impact on traffic safety, operating a vehicle with such problems is not prohibited.
Monitoring the condition of the vehicle while driving plays an important role in suspension maintenance. Creaks, noises and knocks in the suspension should alert and convince the driver of the need for service. And long-term operation of the car will force it to use a radical method - “change the suspension all around,” that is, replace almost all the parts of both the front and rear suspension.
The set of components and assemblies of a vehicle that ensures its movement is called the chassis. The main components of the chassis are the front and rear suspension and wheels. In addition, the vehicle's chassis includes several additional devices: elastic and damping elements, guides, anti-roll bars, tires and wheel supports. The schematic diagram of the car's chassis is as follows.
Car chassis diagram
To give our article greater practical value, we will consider the design of the chassis using the example of one of the most popular cars among domestic motorists - the VAZ 2109.
Front axle
The front axle of the “nine” has a telescopic suspension equipped with coil springs and hydraulic shock absorbers. The transverse arm is of lower design, equipped with braces and anti-roll bars.

Due to the use of a front-wheel drive design on this car model, the technical complexity of the front axle, as one of the main elements of the chassis, is quite high, despite the relatively small number of components that make up the structure. It consists of:
Struts with shock absorbers.
Cross lever.
Steering knuckle.
Stretch systems.
Mounting units to the body (transmission).
Rear axle
The design of the rear axle is much simpler, since it does not contain elements associated with the transmission (with the exception of rear-wheel drive vehicles). In addition, the rear axle bears a smaller load than the front part of the chassis. The relatively mild operating mode allowed the developers to significantly simplify both the circuit diagram of this unit and its design.
A car suspension is a set of elements that provide an elastic connection between the body (frame) and the wheels (axles) of the car. Mainly, the suspension is designed to reduce the intensity of vibration and dynamic loads (shocks, shocks) acting on a person, the transported cargo or structural elements of the car when it moves on an uneven road. At the same time, it must ensure constant contact of the wheel with the road surface and effectively transmit driving force and braking force without deflecting the wheels from the corresponding position. Correct operation of the suspension makes driving comfortable and safe. Despite its apparent simplicity, the suspension is one of the most important systems of a modern car and has undergone significant changes and improvements over the history of its existence.
History of appearance
Attempts to make the movement of a vehicle softer and more comfortable were made in carriages. Initially, the wheel axles were rigidly attached to the body, and every unevenness in the road was transmitted to the passengers sitting inside. Only soft cushions on the seats could increase the level of comfort.
Dependent suspension with transverse spring arrangement
The first way to create an elastic “layer” between the wheels and the carriage body was the use of elliptical springs. Later, this solution was borrowed for the car. However, the spring had already become semi-elliptical and could be installed transversely. A car with such a suspension handled poorly even at low speed. Therefore, springs soon began to be installed longitudinally on each wheel.
The development of the automotive industry has also led to the evolution of the suspension. Currently, there are dozens of their varieties.
Basic functions and characteristics of a car suspension
Each suspension has its own characteristics and performance qualities, which directly affect the handling, comfort and safety of passengers. However, any suspension, regardless of its type, must perform the following functions:
- Absorbs shocks and shocks from the road to reduce loads on the body and increase driving comfort.
- Stabilizing the vehicle while driving by ensuring constant contact of the wheel tire with the road surface and limiting excessive body roll.
- Saving the specified movement geometry and wheel position to maintain steering precision while driving and braking.
 Drift car with rigid suspension
Drift car with rigid suspension The car's rigid suspension is suitable for dynamic driving, which requires an instant and precise reaction to the driver's actions. It provides low ground clearance, maximum stability, resistance to body roll and sway. Mainly used on sports cars.
 Luxury car with energy-intensive suspension
Luxury car with energy-intensive suspension Most passenger cars use soft suspension. It smooths out unevenness as much as possible, but makes the car somewhat rolly and worse to control. If adjustable stiffness is required, a coil suspension is mounted on the vehicle. It consists of shock absorber struts with variable spring tension.
 SUV with long travel suspension
SUV with long travel suspension Suspension travel is the distance from the highest position of the wheel during compression to the lowest position when the wheels are suspended. Suspension travel largely determines the “off-road” capabilities of the car. The larger its value, the greater the obstacle that can be overcome without hitting the limiter or without sagging the drive wheels.
Suspension device
Any car suspension consists of the following main elements:
- Elastic device– absorbs loads from uneven road surfaces. Types: springs, springs, pneumatic elements, etc.
- Damping device— dampens body vibrations when driving over uneven surfaces. Types: all types.
- Guide device—ensures the specified movement of the wheel relative to the body. Kinds: levers, transverse and reaction rods, springs. To change the direction of influence on the damping element, pull-rod and push-rod sports suspensions use rockers.
- Anti-roll bar— reduces lateral body roll.
- Rubber-metal joints— provide an elastic connection of suspension elements with the body. Partially cushions, softens shocks and vibrations. Types: silent blocks and bushings.
- Suspension travel limiters- limit suspension travel in extreme positions.
Classification of pendants
Basically, suspensions are divided into two large types: and independent. This classification is determined by the kinematic diagram of the suspension guide device.
Dependent suspension
The wheels are rigidly connected by means of a beam or continuous bridge. The vertical position of a pair of wheels relative to the common axis does not change, the front wheels are swivel. The rear suspension design is similar. It can be spring, spring or pneumatic. If springs or pneumatic bellows are installed, it is necessary to use special rods to secure the bridges from movement.
 Differences between dependent and independent suspension
Differences between dependent and independent suspension - simple and reliable in operation;
- high load capacity.
- poor handling;
- poor stability at high speeds;
- less comfort.
Independent suspension
The wheels can change their vertical position relative to each other while remaining in the same plane.
- good handling;
- good vehicle stability;
- great comfort.
- more expensive and complex design;
- less reliability during operation.
 Semi-independent suspension
Semi-independent suspension Semi-independent suspension or torsion beam- This is an intermediate solution between dependent and independent suspension. The wheels still remain connected, but there is the possibility of them moving slightly relative to each other. This property is ensured due to the elastic properties of the U-shaped beam connecting the wheels. This suspension is mainly used as a rear suspension for budget cars.
Types of independent suspensions
McPherson
- the most common front axle suspension of modern cars. The lower arm is connected to the hub via a ball joint. Depending on its configuration, longitudinal jet thrust can be used. A shock absorber strut with a spring is attached to the hub assembly, its upper support is fixed to the body.

The transverse link, attached to the body and connecting both levers, is a stabilizer that counteracts the roll of the car. The lower ball joint and shock absorber cup bearing allow the wheel to turn.
The rear suspension parts are made according to the same principle, the only difference is that the wheels cannot be turned. The lower arm has been replaced with longitudinal and transverse rods that secure the hub.
- simplicity of design;
- compactness;
- reliability;
- inexpensive to manufacture and repair.
- average handling.
Double wishbone front suspension
More efficient and complex design. The upper mounting point of the hub is the second wishbone. A spring or torsion bar can be used as an elastic element. The rear suspension has a similar structure. This type of suspension design ensures better vehicle handling.
Air suspension
 Air suspension
Air suspension The role of springs in this suspension is performed by pneumatic cylinders with compressed air. It is possible to adjust the height of the body. It also improves ride quality. Used on luxury cars.
Hydraulic suspension
 Adjusting the height and stiffness of Lexus hydraulic suspension
Adjusting the height and stiffness of Lexus hydraulic suspension The shock absorbers are connected to a single closed circuit with hydraulic fluid. makes it possible to adjust the rigidity and ride height. If the car has control electronics, as well as functions, it independently adapts to road and driving conditions.
Sports independent suspensions
 Coil suspension (coilovers)
Coil suspension (coilovers) Helical suspension, or coilovers, are shock-absorbing struts with the ability to adjust the stiffness directly on the car. Thanks to the threaded connection of the lower spring stop, you can adjust its height, as well as the amount of ground clearance.